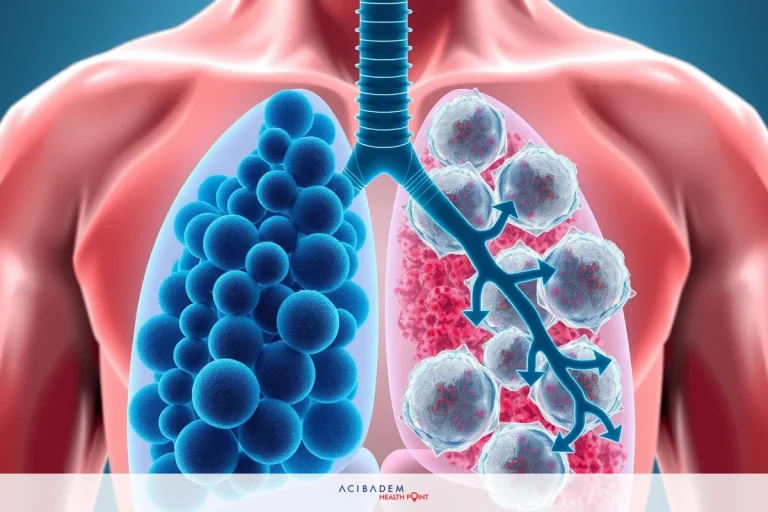
What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer? Lung cancer can be a daunting topic. You might have heard of small cell and non-small cell types but what sets them apart? Small cell lung cancer grows fast and spreads quickly. It’s aggressive.
Non-small cell lung cancer, on the other hand, grows more slowly. It’s more common too. Different treatment options exist for each type.
Understanding these differences helps in making informed decisions. Curious about how doctors diagnose or treat these cancers?
What is Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Small cell lung cancer is a fast-growing type of lung cancer. It often spreads quickly to other parts of the body. This makes it different from non-small cell lung cancer. The rapid growth can be alarming. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
People with small cell lung cancer might not notice symptoms at first. When they do, the signs can include cough, chest pain, or trouble breathing. These symptoms are easy to overlook but should not be ignored. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
Doctors use tests like biopsies and scans to diagnose this type of cancer. Early detection is key for better outcomes. Treatment usually involves chemotherapy and radiation therapy because surgery is less common for small cell lung cancer. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
This kind of lung cancer requires quick action due to its aggressive nature. Understanding its fast pace helps in making informed choices about care options available for patients facing this diagnosis. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
What is Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?
Non-small cell lung cancer grows more slowly than small cell lung cancer. It is the most common type of lung cancer. This makes it different from its fast-growing counterpart small cell lung cancer. People with this type might not see symptoms right away.
Symptoms can include cough, weight loss, or chest pain. These signs often appear gradually over time. Unlike other types non-small cell lung cancer gives a bit more warning.
Doctors use imaging tests and biopsies to diagnose non-small cell lung cancer. Early detection remains crucial here as well for better treatment outcomes.
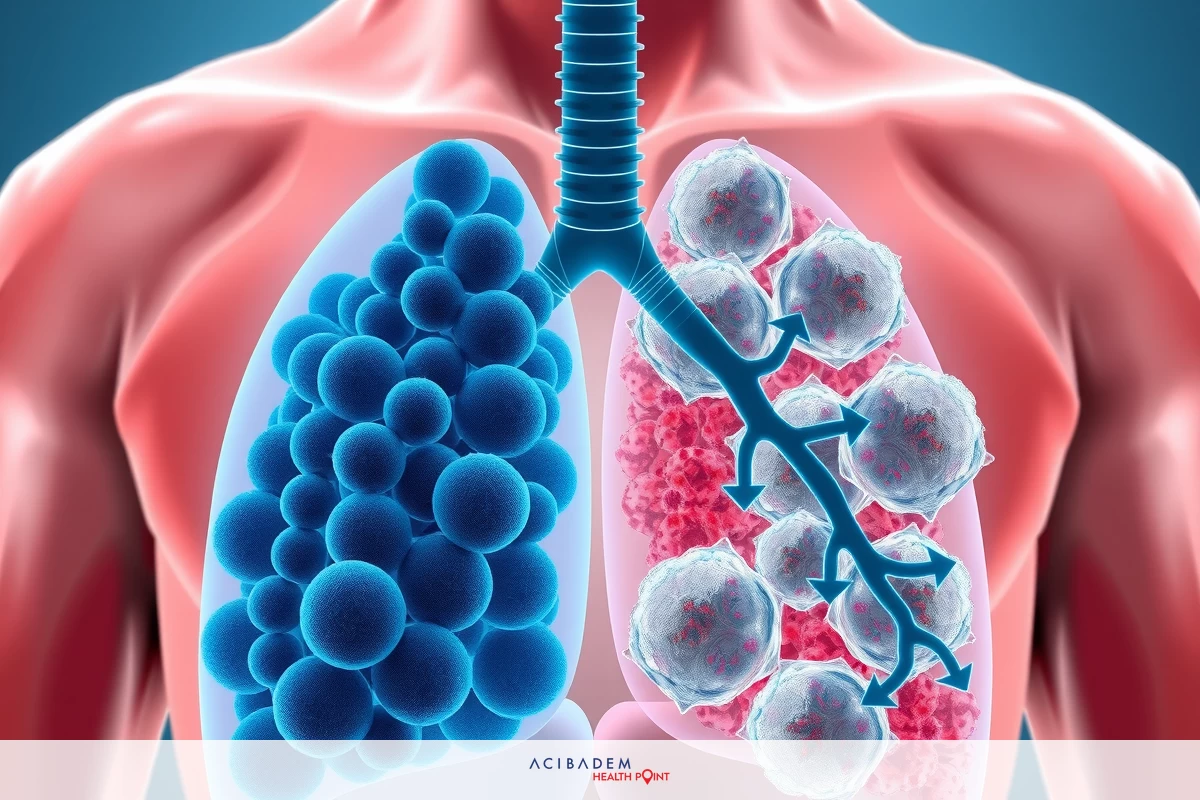
Treatment options are various and can include surgery, targeted therapy, and sometimes immunotherapy. Because it grows slowly patients have more choices for care plans tailored to their needs.
How Are They Diagnosed?
Doctors use tests like biopsies and imaging scans to diagnose both types of lung cancer. This process helps them understand if it’s small cell or non-small cell lung cancer. Imaging scans include CT and PET scans. These scans provide detailed pictures of the lungs.
Biopsies involve taking a small sample of tissue from the lung. The sample is then examined under a microscope. This test can confirm the type of lung cancer present in the body. It also shows how far it has spread which is crucial for treatment planning.
In addition to these tests doctors may do blood tests to check overall health. Sometimes they use bronchoscopy where a thin tube goes into the lungs through the nose or mouth to collect samples directly from inside airways.
Early diagnosis plays an important role in effective treatment plans for both small cell and non-small cell lung cancers as well as other types. Hence knowing what kind one has makes all difference when deciding on suitable treatments moving forward.
Treatment Options for Small Cell Lung Cancer
Treatments for small cell lung cancer include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and sometimes surgery. Chemotherapy is often the first choice because it targets fast-growing cells throughout the body. This method uses strong drugs to kill cancer cells.
Radiation therapy focuses on specific areas of the body where cancer is present. It helps shrink tumors and relieve symptoms like pain or difficulty breathing. This treatment works well when combined with chemotherapy.
Surgery is less common for small cell lung cancer but can be an option in early stages. If the tumor has not spread far doctors may remove part of a lung or even an entire lobe.
Other treatments might include immunotherapy which boosts the body’s natural defenses against cancer cells. This newer approach shows promise in some cases as part of comprehensive care plans tailored individually based on each patient’s unique needs.
Treatment Options for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer treatments may include surgery, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Surgery is often the first line of treatment if the cancer is detected early. Doctors might remove a part or even an entire lobe of the lung. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
For those not suited for surgery targeted therapy is an option. This treatment uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells while sparing healthy ones. It’s effective because it focuses on specific molecules involved in tumor growth. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight off cancer cells more effectively. This method can be used alone or combined with other treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy for better results. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
Each patient’s treatment plan varies based on their unique case and health status. Thus doctors tailor these plans individually ensuring optimal care suited best towards achieving successful outcomes. What is the difference between small cell and non- small cell lung cancer?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the main types of lung cancer? A: The main types are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer.
Q: How is small cell lung cancer different from non-small cell lung cancer? A: Small cell lung cancer grows fast and spreads quickly. Non-small cell lung cancer grows more slowly and is more common.
Q: What treatments are available for small cell lung cancer? A: Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and sometimes surgery.